Defining Dysregulation: Understanding Emotional and Behavioral Challenges
 Defining dysregulation is an important concept in understanding emotional and behavioral challenges. Dysregulation is a term used to describe a state of emotional and behavioral instability, which can manifest in a variety of ways. It is often associated with mental health issues such as anxiety, depression, and trauma. Dysregulation can also be seen in individuals who have difficulty managing their emotions, behaviors, and reactions to stress. This article will explore the concept of dysregulation, its causes, and how it can be addressed. It will also discuss the importance of recognizing and understanding dysregulation in order to provide effective support and treatment.
Defining dysregulation is an important concept in understanding emotional and behavioral challenges. Dysregulation is a term used to describe a state of emotional and behavioral instability, which can manifest in a variety of ways. It is often associated with mental health issues such as anxiety, depression, and trauma. Dysregulation can also be seen in individuals who have difficulty managing their emotions, behaviors, and reactions to stress. This article will explore the concept of dysregulation, its causes, and how it can be addressed. It will also discuss the importance of recognizing and understanding dysregulation in order to provide effective support and treatment.
Exploring the Causes of Dysregulation: Examining the Role of Genetics, Environment, and Developmental Factors
The dysregulation of behavior is a complex phenomenon that can have a significant impact on an individual’s life. It is important to understand the causes of dysregulation in order to develop effective interventions and treatments. In this article, we will explore the role of genetics, environment, and developmental factors in the development of dysregulation.
Genetics play an important role in the development of dysregulation. Research has shown that certain genetic variations can increase the risk of developing dysregulation. For example, a study of twins found that those with a genetic predisposition to dysregulation were more likely to display dysregulated behavior than those without the genetic predisposition. Additionally, research has shown that certain genetic variations can influence the severity of dysregulation.
The environment can also play a role in the development of dysregulation. Environmental factors such as poverty, trauma, and neglect can increase the risk of developing dysregulation. Additionally, research has shown that certain environmental factors can influence the severity of dysregulation. For example, a study of children in foster care found that those who experienced more traumatic events were more likely to display more severe dysregulation.
Finally, developmental factors can also contribute to the development of dysregulation. Research has shown that certain developmental delays can increase the risk of developing dysregulation. Additionally, research has shown that certain developmental delays can influence the severity of dysregulation. For example, a study of children with autism found that those with more severe developmental delays were more likely to display more severe dysregulation.
In conclusion, genetics, environment, and developmental factors all play a role in the development of dysregulation. It is important to understand the causes of dysregulation in order to develop effective interventions and treatments. By understanding the role of genetics, environment, and developmental factors, we can better understand the causes of dysregulation and develop more effective interventions and treatments.
Understanding Dysregulation: Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Emotional and Behavioral Challenges
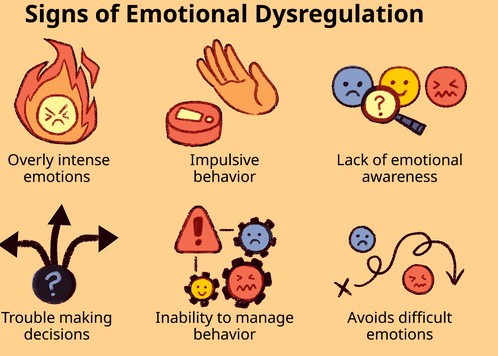
Understanding dysregulation—the inability to effectively manage emotions and behaviors—is an important part of helping individuals with emotional and behavioral challenges. Dysregulation can manifest in a variety of ways, including difficulty controlling emotions, difficulty managing behaviors, and difficulty regulating attention. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of dysregulation can help individuals, families, and professionals better understand and support those with emotional and behavioral challenges.
Signs and symptoms of dysregulation can vary depending on the individual and the situation. Generally, individuals with dysregulation may experience difficulty controlling their emotions, difficulty managing their behaviors, and difficulty regulating their attention.
Emotionally, individuals with dysregulation may experience intense emotions, such as anger, sadness, or fear, that are difficult to manage. They may also have difficulty recognizing and expressing their emotions in a healthy way. Behaviors associated with dysregulation may include aggression, impulsivity, or self-injurious behaviors. Attentional dysregulation may manifest as difficulty focusing, difficulty staying on task, or difficulty following directions.
It is important to note that dysregulation is not a diagnosis, but rather a symptom of a variety of mental health conditions. It is also important to recognize that dysregulation can be a normal part of development, and that it is not necessarily indicative of a mental health disorder.
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of dysregulation can help individuals, families, and professionals better understand and support those with emotional and behavioral challenges. With the right support, individuals with dysregulation can learn to manage their emotions and behaviors in a healthy way.In conclusion, understanding the concept of dysregulation is essential for helping individuals with emotional and behavioral challenges. By recognizing the signs of dysregulation, professionals can provide the necessary support and interventions to help individuals manage their emotions and behaviors. Additionally, understanding the underlying causes of dysregulation can help professionals develop more effective interventions and strategies to help individuals better manage their emotions and behaviors.