Skin Infections: Causes and How to Treat Them
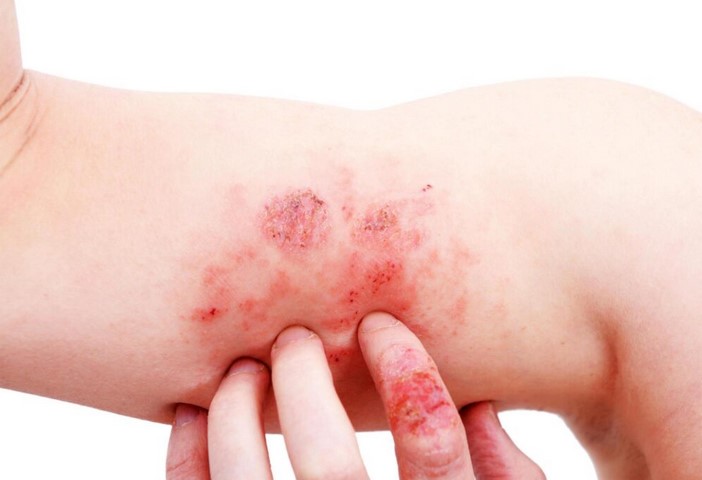
Skin infections are among the most common health issues people experience, affecting individuals of all ages. These infections can range from minor irritations to serious conditions that require medical attention. Whether caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites, skin infections can be uncomfortable and even lead to long-term complications if not treated properly. This article will explore the causes, symptoms, types, and effective treatment options for skin infections. Understanding these factors is essential for maintaining healthy skin and preventing the spread of these infections.
Causes of Skin Infections
Skin infections are primarily caused by microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, viruses, and parasites that enter the body through cuts, abrasions, or other openings in the skin. The skin serves as a protective barrier, but when this barrier is broken, harmful pathogens can enter, leading to infections. Below are the common causes of skin infections:
Bacterial Infections
Bacteria are the most common culprits behind skin infections. The most well-known bacteria responsible for skin infections are Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. These bacteria can invade the skin through cuts, insect bites, or even hair follicles.
- Impetigo: This highly contagious skin infection is most common in children and is caused by Streptococcus or Staphylococcus bacteria. It typically appears as red sores or blisters that can ooze and form a yellowish crust.
- Cellulitis: Caused by Streptococcus or Staphylococcus bacteria, cellulitis affects the deeper layers of the skin, resulting in redness, swelling, and pain. It can lead to severe complications if left untreated.
- Folliculitis: This infection occurs when hair follicles become inflamed, often due to bacterial infection. It can cause small red bumps or pimples around the infected follicles.
Fungal Infections
Fungal infections are another common cause of skin issues, and they often thrive in warm, moist environments. Common fungal infections include:
- Ringworm: Despite its name, ringworm is not caused by a worm but by a fungal infection. It causes red, circular patches with a clear center on the skin, often seen in athletes or people with sweaty skin.
- Athlete’s Foot: A common fungal infection that affects the feet, especially the spaces between the toes. It is usually accompanied by itching, burning, and peeling skin.
- Candidiasis: Caused by an overgrowth of the yeast Candida, this fungal infection can affect various parts of the body, including the skin, mouth, and genital areas.
Viral Infections
Viral skin infections are caused by viruses that affect the skin’s surface. Some of the most common viral infections include:
- Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV): This virus causes cold sores and can affect both the mouth (oral herpes) and genital areas (genital herpes). The virus causes painful blisters that can recur periodically.
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV): This virus causes warts, which can appear on the hands, feet, or genital area. Warts are usually non-cancerous but can be unsightly and uncomfortable.
- Chickenpox (Varicella): Chickenpox is a viral infection that causes itchy, red spots and blisters. It is highly contagious and is more common in children, though adults can contract it as well.
Parasitic Infections
Parasites can also cause skin infections. Common parasitic infections include:
- Scabies: Caused by tiny mites that burrow under the skin, scabies results in intense itching and the formation of small red bumps or blisters.
- Lice: Lice are small parasites that live in the hair and on the scalp, causing itching and irritation. They are typically spread through close contact or sharing personal items like combs or hats.
Symptoms of Skin Infections
The symptoms of skin infections can vary depending on the type of infection, but some common signs include:
- Redness and swelling of the affected area
- Pain, tenderness, or warmth in the infected region
- Itching or burning sensation
- Pus or fluid drainage from sores, blisters, or cuts
- Crusting or scabbing over lesions
- Fever (in severe cases)
- Skin that feels hot to the touch
It’s important to consult a healthcare provider if you notice any of these symptoms, especially if the infection is spreading or becoming more painful. Delayed treatment can lead to complications, such as cellulitis or sepsis.
How to Treat Skin Infections
Treatment for skin infections depends on the type of infection and its severity. In many cases, timely intervention can help alleviate symptoms and prevent the infection from spreading. Below are some general treatment options for different types of skin infections:
1. Bacterial Infections
For bacterial infections, antibiotics are commonly prescribed. The doctor may recommend topical antibiotics, such as Neosporin, for mild cases. However, more severe infections may require oral or intravenous antibiotics. It’s essential to complete the entire course of antibiotics, even if the symptoms disappear before finishing the medication, to ensure the infection is fully treated.
2. Fungal Infections
Antifungal treatments are used to treat fungal infections. These can be in the form of topical creams, oral medications, or even medicated shampoos, depending on the severity and location of the infection. For example, athlete’s foot can be treated with antifungal creams, while more persistent fungal infections may require oral medications like fluconazole.
3. Viral Infections
Viral infections, such as cold sores or genital herpes, often don’t have a permanent cure. However, antiviral medications can help reduce the severity and duration of outbreaks. For instance, medications like acyclovir can be prescribed to reduce the frequency and intensity of cold sores. Warts caused by HPV can be treated with cryotherapy, salicylic acid, or other topical treatments.
4. Parasitic Infections
Parasitic infections like scabies and lice require medications that specifically target the parasites. For scabies, topical creams like permethrin are commonly used, while lice can be treated with medicated shampoos and combing through the hair to remove the insects and eggs.
5. Home Remedies and Prevention
While medical treatment is often necessary, there are several home remedies that can help alleviate symptoms. For example, applying cool compresses to the affected area can reduce inflammation and discomfort. Additionally, over-the-counter hydrocortisone creams or calamine lotion can help soothe itching. Keeping the skin clean and dry is also crucial in preventing infections from worsening or recurring.
Conclusion
Skin infections can be bothersome, but with the right treatment, they are typically manageable. It’s essential to recognize the symptoms of skin infections early and seek appropriate care to prevent further complications. Whether the infection is caused by bacteria, fungi, viruses, or parasites, understanding the cause and the best treatment options will help in speeding up recovery. If you experience severe or persistent symptoms, it’s always best to consult a healthcare provider to ensure the most effective treatment. Taking preventive measures and maintaining proper hygiene can help reduce the risk of developing skin infections in the future.